What Substances Dissolve In Water
Learning Objective
- Explain why some molecules exercise not deliquesce in h2o.
Key Points
- Water dissociates salts by separating the cations and anions and forming new interactions between the water and ions.
- Water dissolves many biomolecules, because they are polar and therefore hydrophilic.
Terms
- dissociationThe process by which a compound or complex body breaks up into simpler constituents such as atoms or ions, usually reversibly.
- hydration shellThe term given to a solvation vanquish (a structure composed of a chemical that acts as a solvent and surrounds a solute species) with a water solvent; as well referred to as a hydration sphere.
Examples
- Sugar, sodium chloride, and hydrophilic proteins are all substances that dissolve in h2o.
- Oils, fats, and certain organic solvents practise not deliquesce in water because they are hydrophobic.
Water'due south Solvent Properties
Water, which not only dissolves many compounds but too dissolves more substances than any other liquid, is considered the universal solvent. A polar molecule with partially-positive and negative charges, it readily dissolves ions and polar molecules. Water is therefore referred to as a solvent: a substance capable of dissolving other polar molecules and ionic compounds. The charges associated with these molecules form hydrogen bonds with water, surrounding the particle with h2o molecules. This is referred to equally a sphere of hydration, or a hydration beat out, and serves to keep the particles separated or dispersed in the water.
When ionic compounds are added to h2o, private ions collaborate with the polar regions of the water molecules during the dissociation process, disrupting their ionic bonds. Dissociation occurs when atoms or groups of atoms break off from molecules and form ions. Consider table salt (NaCl, or sodium chloride): when NaCl crystals are added to h2o, the molecules of NaCl dissociate into Na+ and Cl– ions, and spheres of hydration class effectually the ions. The positively-charged sodium ion is surrounded past the partially-negative charge of the h2o molecule's oxygen; the negatively-charged chloride ion is surrounded by the partially-positive charge of the hydrogen in the water molecule.
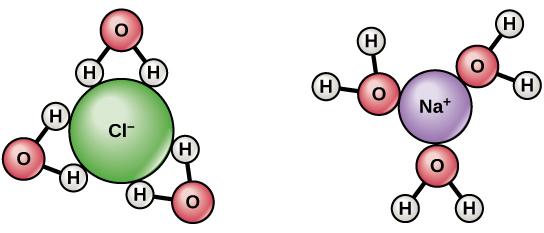
Since many biomolecules are either polar or charged, water readily dissolves these hydrophilic compounds. Water is a poor solvent, however, for hydrophobic molecules such as lipids. Nonpolar molecules experience hydrophobic interactions in water: the h2o changes its hydrogen bonding patterns effectually the hydrophobic molecules to produce a cage-like structure chosen a clathrate. This change in the hydrogen-bonding design of the water solvent causes the organization's overall entropy to profoundly decrease, as the molecules become more ordered than in liquid water. Thermodynamically, such a large subtract in entropy is not spontaneous, and the hydrophobic molecule will not dissolve.
Bear witness Sources
Licenses and Attributions
What Substances Dissolve In Water,
Source: https://www.coursehero.com/study-guides/introchem/waters-solvent-properties/
Posted by: ferrarifichalfic.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Substances Dissolve In Water"
Post a Comment