Sign Of A Chemical Reaction
CBSE Course 10 Science Notes Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Pdf gratuitous download is part of Class x Science Notes for Quick Revision. Here we have given NCERT Grade x Scientific discipline Notes Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations.
According to new CBSE Exam Pattern, MCQ Questions for Course x Scientific discipline pdf Carries xx Marks.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chemical Reactions and Equations: Counterbalanced and unbalanced chemic equations and balancing of chemical equations.
What is a chemic reaction Class 10?
Chemical Reaction: The transformation of chemic substance into some other chemical substance is known as Chemical Reaction. For case: Rusting of iron, the setting of milk into curd, digestion of food, respiration, etc.
In a chemic reaction, a new substance is formed which is completely different in properties from the original substance, so in a chemical reaction, a chemical change takes place.
Simply a rearrangement of atoms takes place in a chemic reaction.
- The substances which have part in a chemic reaction are called reactants.
- The new substances produced as a result of a chemical reaction are called products.
Instance: The burning of magnesium in the air to form magnesium oxide is an example of a chemical reaction.
2Mg(south) + O2(g) \(\underrightarrow { \triangle }\) 2MgO(s)
Earlier burning in air, the magnesium ribbon is cleaned by rubbing with sandpaper.
This is done to remove the protective layer of basic magnesium carbonate from the surface of the magnesium ribbon.
Reactant: Substances which accept part in a chemical reaction are called reactants.
Instance: Mg and O2.
Production: New substance formed after a chemic reaction is called a product.
Example: MgO.
Characteristics of Chemical Reactions :
(i) Evolution of gas: The chemic reaction between zinc and dilute sulphuric acrid is characterised past the evolution of hydrogen gas.
Zn(s) + HiiAnd then4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(k) ↑
(ii) Change in Colour: The chemical reaction between citric acid and purple coloured potassium permanganate solution is characterised by a change in colour from purple to colourless.
The chemical reaction between sulphur dioxide gas and acidified potassium dichromate solution is characterized by a change in colour from orangish to green.
(3) Modify in state of substance: The combustion reaction of candle wax is characterised by a alter in state from solid to liquid and gas (considering the wax is a solid, water formed by the combustion of wax is a liquid at room temperature whereas, carbon dioxide produced past the combustion of wax is a gas). There are some chemic reactions which tin evidence more than one characteristics.
(four) Change in temperature: The chemical reaction betwixt quick lime h2o to form slaked lime is characterized by a change in temperature (which is a rise in temperature).
The chemical reaction between zinc granules and dilute sulphuric acid is also characterised by a alter in temperature (which is a rise in temperature).
(v) Formation of precipitate: The chemical reaction between sulphuric acrid and barium chloride solution is characterised by the formation of a white precipitate of barium sulphate.
BaClii(aq) + H2SOfour(aq) → BaSO4(s) (ppt) + 2HCl(aq)
What is a chemic Equation Class 10?
Chemical Equation: Representation of chemic reaction using symbols and formulae of the substances is chosen Chemical Equation.
Instance: A + B → C + D
In this equation, A and B are chosen reactants and C and D are chosen the products. The arrow shows the direction of the chemical reaction. Status, if whatsoever, is written generally above the arrow.
When hydrogen reacts with oxygen, it gives water. This reaction can exist represented by the following chemical equation:
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Water
Htwo + Oii → H2O
In the commencement equation, words are used and in second, symbols of substances are used to write the chemical equation. For convenience, the symbol of substance is used to stand for chemical equations.
A chemical equation is a way to represent the chemical reaction in a concise and informative way.
A chemic equation tin be divided into two types: Counterbalanced Chemical Equation and Unbalanced Chemical Equation.
(a) Balanced Chemical Equation: A counterbalanced chemic equation has the number of atoms of each element equal on both sides.
Example: Zn + HtwoAnd then4 → ZnSOfour + Htwo
In this equation, numbers of zinc, hydrogen and sulphate are equal on both sides, so it is a Balanced Chemical Equation.
Co-ordinate to the Police of Conservation of Mass, mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. To obey this law, the total mass of elements nowadays in reactants must exist equal to the full mass of elements present in products.
(b) Unbalanced Chemical Equation: If the number of atoms of each element in reactants is not equal to the number of atoms of each element present in the product, then the chemical equation is called Unbalanced Chemical Equation.
Example: Fe + H2O → Fe3Oiv + Hii
In this example, a number of atoms of elements are non equal on two sides of the reaction. For example; on the left-manus side only ane iron atom is present, while three iron atoms are present on the right-hand side. Therefore, it is an unbalanced chemical equation.
Balancing a Chemical Equation: To remainder the given or any chemical equation, follow these steps:
Fe + H2O → Iron3O4 + Htwo
Write the number of atoms of elements present in reactants and in products in a table as shown here.
| Name of atom | No. of atoms in the reactant | No. of atoms in the product |
| Iron | 1 | 3 |
| Hydrogen | ii | 2 |
| Oxygen | 1 | iv |
Remainder the atom which is maximum in number on either side of a chemic equation.
In this equation, the number of oxygen atom is the maximum on the RHS.
To balance the oxygen, one needs to multiply the oxygen on the LHS by iv, so that, the number of oxygen atoms becomes equal on both sides.
Fe + 4 × H2O → Atomic number 26iiiO4 + Hii
Now, the number of hydrogen atoms becomes 8 on the LHS, which is more than that on the RHS. To residue it, one needs to multiply the hydrogen on the RHS past 4.
Atomic number 26 + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + four × H2
After that, the number of oxygen and hydrogen atoms becomes equal on both sides. The number of iron is ane on the LHS, while information technology is three on the RHS. To rest information technology, multiply the iron on the LHS by 3.
three × Iron + 4 × H2O → FethreeOfour + 4 × H2
At present the number of atoms of each element becomes equal on both sides. Thus, this equation becomes a counterbalanced equation.
| Name of cantlet | No. of atoms in the reactant | No. of atoms in the product |
| Iron | iii | three |
| Hydrogen | 8 | eight |
| Oxygen | 4 | iv |
Afterwards balancing, the above equation can be written as follows:
3Fe + 4HiiO → FeiiiO4 + 4H2.
To Make Equations More Informative:
Writing the symbols of physical states of substances in a chemical equation:
By writing the concrete states of substances, a chemical equation becomes more informative.
- Gaseous state is represented by symbol (g).
- Liquid country is represented past symbol (50).
- Solid state is written by symbol (s).
- Aqueous solution is written by symbol (aq).
- Writing the condition in which reaction takes place: The condition is mostly written to a higher place and/or below the arrow of a chemical equation.
Thus, by writing the symbols of the physical country of substances and condition nether which reaction takes place, a chemical equation can be made more informative.
What are the types of a chemical reaction Class ten?
Types of Chemical Reactions: Combination Reaction, Decomposition Reaction, Deportation Reaction, Double Displacement Reaction, Neutralization Reactions, Exothermic – Endothermic Reactions and Oxidation-Reduction Reactions.
Types of Chemic Reactions:
Chemical reactions can be classified in post-obit types:
(i) Combination Reaction: Reactions in which ii or more reactants combine to grade 1 production are chosen Combination Reactions.
A general combination reaction can be represented by the chemical equation given here:
A + B → AB
Examples:
When magnesium is burnt in the air (oxygen), magnesium oxide is formed. In this reaction, magnesium is combined with oxygen.
Mg(s) + O2(chiliad) → 2MgO(southward)
Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium Oxide
When carbon is burnt in oxygen (air), carbon dioxide is formed. In this reaction, carbon is combined with oxygen.
C (s) + Oii(1000) → CO2(g)
Carbon + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide
(ii) Decomposition Reaction: Reactions in which one compound decomposes in two or more compounds or elements are known every bit Decomposition Reaction. A decomposition reaction is just the opposite of combination reaction.
A general decomposition reaction can exist represented as follows :
AB → A + B
Examples:
When calcium carbonate is heated, it decomposes into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
CaCO3(s) \(\underrightarrow { heat }\) CaO(s) + CO2(yard)
Calcium carbonate → Calcium oxide + Carbon dioxide
When ferric hydroxide is heated, it decomposes into ferric oxide and water
2Fe(OH)three(south) \(\underrightarrow { \triangle }\) Fe2O3(s) + 3H2O(l)
Thermal Decomposition: The decomposition of a substance on heating is known as Thermal Decomposition.
Example: 2Pb(NO3)two(due south) \(\underrightarrow { heat }\) 2PbO(s) + 4NOtwo(g) + O2(g)
Electrolytic Decomposition: Reactions in which compounds decompose into simpler compounds because of passing of electricity, are known as Electrolytic Decomposition. This is also known as Electrolysis.
Example: When electricity is passed in water, it decomposes into hydrogen and oxygen.
2H2O(l) \(\xrightarrow [ Electrolysis ]{ Electric\quad Electric current }\) 2H2(g) + Oii(g)
Photolysis or Photo Decomposition Reaction: Reactions in which a compound decomposes because of sunlight are known equally Photolysis or Photo Decomposition Reaction.
Instance: When silver chloride is put in sunlight, it decomposes into silver metal and chlorine gas.
2AgCl(due south) (white) \(\underrightarrow { Sunlight }\) 2Ag(s) (grey) + Cl2(k)
Photographic paper has a coat of argent chloride, which turns into greyness when exposed to sunlight. Information technology happens considering silver chloride is colourless while argent is a grey metallic.
(3) Displacement Reaction: The chemical reactions in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from a compound is known as Displacement Reactions. Displacement reactions are also known equally Substitution Reaction or Unmarried Displacement/ replacement reactions.
A full general displacement reaction tin be represented by using a chemic equation as follows :
A + BC → AC + B
Displacement reaction takes identify only when 'A' is more reactive than B. If 'B' is more reactive than 'A', then 'A' volition not readapt 'C' from 'BC' and reaction will not exist taking place.
Examples:
When zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid, it gives hydrogen gas and zinc chloride.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(chiliad)
When zinc reacts with copper sulphate, information technology forms zinc sulphate and copper metal.
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSOiv(aq) + Cu(due south)
(iv) Double Deportation Reaction: Reactions in which ions are exchanged between two reactants forming new compounds are chosen Double Displacement Reactions.
AB + CD → Air conditioning + BD
Examples:
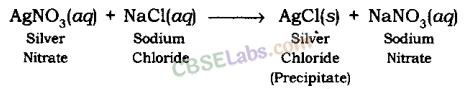
When the solution of barium chloride reacts with the solution of sodium sulphate, white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed along with sodium chloride.
BaCl2(aq) + Na2SOfour(aq) → BaSOfour(s) (Precipitate) + 2NaCl(aq)
When sodium hydroxide (a base) reacts with hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride and h2o are formed.
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Notation: Double Deportation Reaction, in which precipitate is formed, is too known as precipitation reaction. Neutralisation reactions are also examples of double displacement reaction.
Atmospheric precipitation Reaction: The reaction in which precipitate is formed past the mixing of the aqueous solution of two salts is chosen Precipitation Reaction.
Example:
Neutralization Reaction: The reaction in which an acid reacts with a base of operations to grade salt and water by an exchange of ions is called Neutralization Reaction.
Instance:
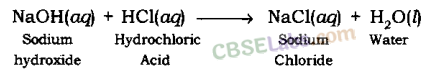
(five) Oxidation and Reduction Reactions:
Oxidation: Addition of oxygen or non-metallic element or removal of hydrogen or metallic element from a compound is known as Oxidation.
Elements or compounds in which oxygen or not-metallic element is added or hydrogen or metallic element is removed are called to be Oxidized.
Reduction: Improver of hydrogen or metal chemical element or removal of oxygen or non-metallic element from a compound is chosen Reduction.
The compound or chemical element which goes under reduction in chosen to be Reduced.
Oxidation and Reduction take place together.
Oxidizing agent:
- The substance which gives oxygen for oxidation is called an Oxidizing agent.
- The substance which removes hydrogen is also chosen an Oxidizing agent.
Reducing agent:
- The substance which gives hydrogen for reduction is called a Reducing agent.
- The substance which removes oxygen is as well called a Reducing agent.
The reaction in which oxidation and reduction both take place simultaneously is called Redox reaction.
When copper oxide is heated with hydrogen, then copper metal and hydrogen are formed.
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
(i) In this reaction, CuO is irresolute into Cu. Oxygen is beingness removed from copper oxide. Removal of oxygen from a substance is chosen Reduction, so copper oxide is being reduced to copper.
(2) In this reaction, Hii is changing to H2O. Oxygen is being added to hydrogen. Addition of oxygen to a substance is called Oxidation, so hydrogen is being oxidised to water.
- The substance which gets oxidised is the reducing agent.
- The substance which gets reduced is the oxidizing agent.
(vi) Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions:
Exothermic Reaction: Reaction which produces energy is called Exothermic Reaction. Most of the decomposition reactions are exothermic.
Example:
Respiration is a decomposition reaction in which energy is released.
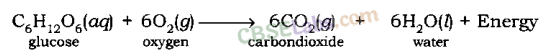
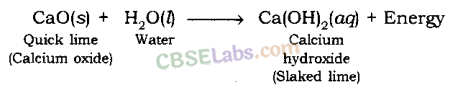
When quick lime (CaO) is added to h2o, information technology releases energy.
Endothermic Reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy is absorbed is chosen Endothermic Reaction.
Example: Decomposition of calcium carbonate.

Effects of Oxidation Reactions in Everyday life: Corrosion and Rancidity.
Corrosion: The process of slow conversion of metals into their undesirable compounds due to their reaction with oxygen, h2o, acids, gases etc. present in the atmosphere is chosen Corrosion.
Case: Rusting of iron.
Rusting: Atomic number 26 when reacts with oxygen and wet forms crimson substance which is called Rust.
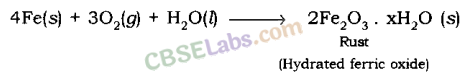
The rusting of atomic number 26 is a redox reaction.
Corrosion (rusting) weakens the iron and steel objects and structures such as railings, car bodies, bridges and ships etc. and cuts short their life.
Methods to Prevent Rusting
- By painting.
- By greasing and oiling.
- By galvanisation.
Corrosion of Copper: Copper objects lose their lustre and polish afterwards some fourth dimension considering the surface of these objects acquires a green coating of basic copper carbonate, CuCOiii.Cu(OH)ii when exposed to air.
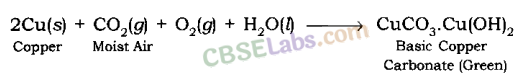
Corrosion of Argent Metal: The surface of silver metal gets tarnished (becomes dull) on exposure to air, due to the formation of a coating of black silvery sulphide(Ag2S) on its surface past the action of H2S gas present in the air.

Rancidity: The sense of taste and odour of food materials containing fat and oil changes when they are left exposed to air for a long time. This is called Rancidity. Information technology is caused due to the oxidation of fat and oil nowadays in food materials.
Methods to prevent rancidity:
- Past calculation anti-oxidant.
- Vacuum packing.
- Replacing air by nitrogen.
- Refrigeration of foodstuff.
1. Chemic Reaction: During chemical reactions, the chemic composition of substances changes or new substances are formed.
2. Chemical Equation: Chemical reactions can be written in chemical equation course which should e'er be balanced.
three. Types of Chemical Reactions:
Combination reaction: A single product is formed from two or more than reactants.
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Decomposition reaction: A single reactant breaks down to yield two or more than products.
- Thermal decomposition: 2Pb(NOtwo)ii → 2PbO + 4NOtwo + O2
- Electrolysis: 2H20 → 2H2 + O2
- Photochemical reaction: 2AgBr → 2Ag + Br2
Displacement reaction: 1 element is displaced by another chemical element.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSOfour + Cu
Double displacement reaction: Exchange of ions between reactants.
AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNOthree
Redox reaction: Both oxidation and reduction take identify simultaneously.
CuO + Htwo → Cu + H2O
Exothermic reaction: A chemic reaction in which estrus energy is evolved.
C + Oii → CO2 (one thousand) + heat
Endothermic reaction: A chemical reaction in which oestrus energy is absorbed.
ZnCO3 + Heat → ZnO + CO2
Redox reaction: Chemical reaction in which both oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously.
four. Oxidation: Reaction that involves the proceeds of oxygen or loss of hydrogen.
5. Reduction: Reaction that shows the loss of oxygen or gain of hydrogen.
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
ZnO is reduced to Zn—reduction. C is oxidized to CO—Oxidation.
six. Effects of Oxidation Reactions in Our Daily Life:
- Corrosion: It is an undesirable change that occurs in metals when they are attacked by moisture, air, acids and bases.
Example, Corrosion (rusting) of Fe: Fe2Othree. nH2O (Hydrated iron oxide) - Rancidity: Undesirable alter that takes identify in oil containing food items due to the oxidation of fat acids.
Preventive methods of rancidity: Adding antioxidants to the nutrient materials, storing food in the closed container, flushing out air with nitrogen gas and refrigeration.
We promise the given CBSE Course x Science Notes Chapter ane Chemic Reactions and Equations Pdf free download volition aid you lot. If y'all accept whatsoever query regarding NCERT Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations, drop a annotate below and we will get dorsum to you at the earliest.
Sign Of A Chemical Reaction,
Source: https://www.learncbse.in/chemical-reactions-and-equations-class-10-notes/
Posted by: ferrarifichalfic.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Sign Of A Chemical Reaction"
Post a Comment